Our work spans from developing foundational meta-science methods to high-resolution mapping of the human exposome and personal health trajectories.
Mapping the Global Exposome-Phenome
An Atlas of Genetic and Environmental Contributions to 560 Phenotypes Lakhani et al., Nature Genetics, 2019 By repurposing U.S. insurance claims, we created a “shared exposome atlas” showing that non-genetic factors are significant drivers of most common diseases.
Altmetric: 874
The Landscape of Genetic Content in the Human Microbiome Tierney et al., Cell Host & Microbe, 2019 Moved beyond species-level taxonomy to a gene-centric view of the microbiome, treating microbial genes as a functional ’omics layer for precision medicine.
An Atlas of Exposome-Phenome Associations Patel et al., Nature Medicine, 2026 (In Press) A decade of research synthesized into a single characterization of the “architecture” of how the environment relates to the clinical phenome, serving as a blueprint for the NEXUS consortium.
Precision Prevention & Predictive Modeling
Polyexposure Scores in Risk Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes He et al., Diabetes Care, 2021 Formalized “polyexposure risk scores” as a clinical counterpart to genetics, quantifying how much incremental information the exposome adds to diabetes prediction.
Using Deep Learning to Predict Abdominal Age from MRI Le Goallec et al., Nature Communications, 2022 Developed AI to predict “organ-specific age,” linking structural changes in the liver and pancreas to metabolic and cardiometabolic risk.
Timing and Consistency of Physical Activity Tian et al., Diabetologia, 2023 Proved that high-resolution behavioral timing (accelerometry) is a critical, modifiable risk factor for diabetes, informing precision lifestyle guidance.
Altmetric: 630
Foundational Meta-Science & Robustness
Vibration of Effects in Observational Research Patel et al., J Clin Epidemiol, 2015 Introduced the “Vibration of Effects” (VoE) framework to quantify how statistical choices change study outcomes. This paper underpins our group’s focus on reproducible research.
Systematically Assessing Drivers of Inconsistency in Metagenomics Tierney et al., PLoS Biology, 2022 We re-analyzed 581 microbiome–disease associations to demonstrate how analytic choices drive conflicting results, providing a template for robust discovery in high-dimensional data.
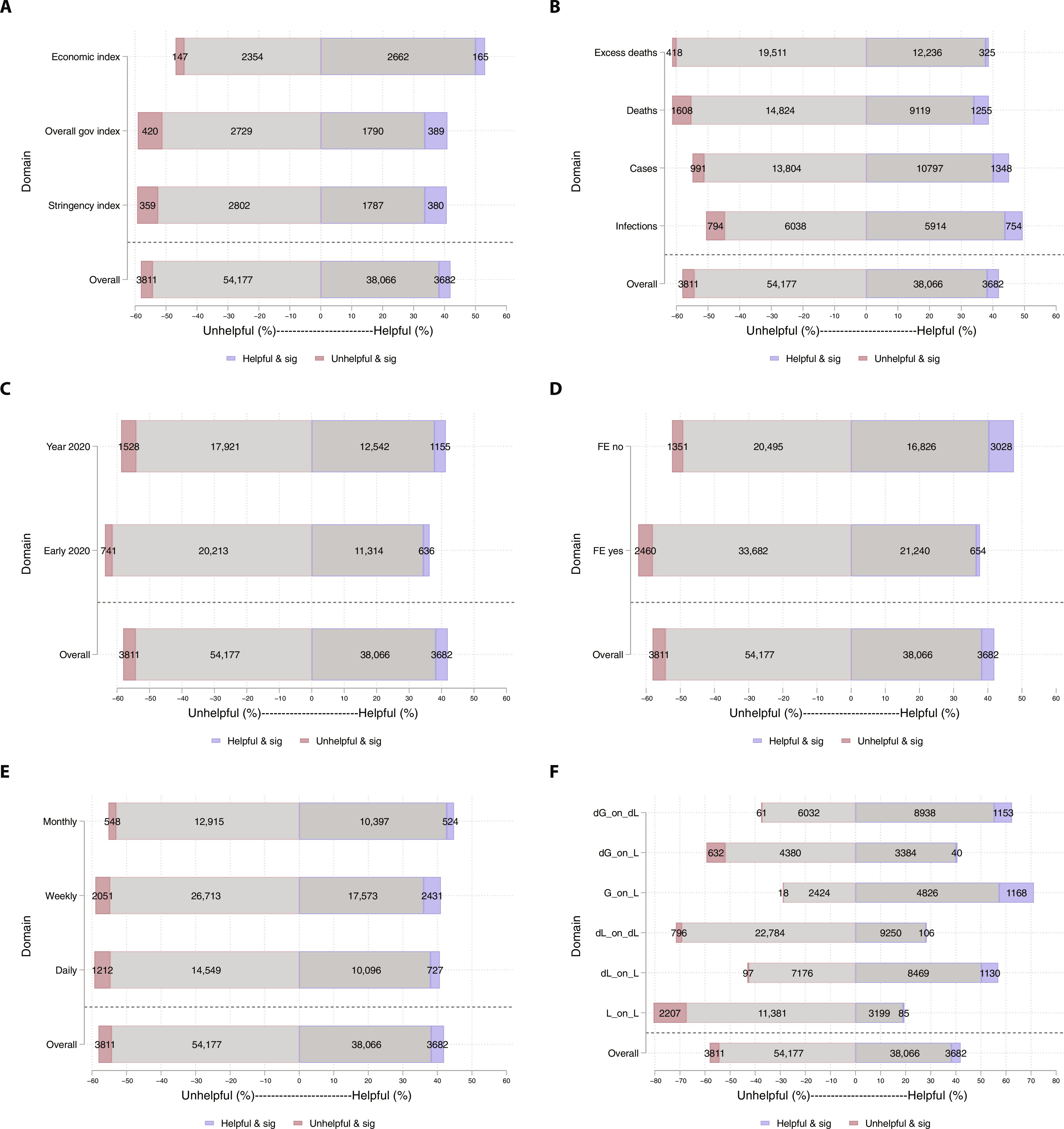
Epidemic outcomes following government responses to COVID-19: Insights from nearly 100,000 models The extent to which responses—such as school closures—were associated with changes in COVID-19 outcomes remains unsettled. Here we use a meta-research approach to examine robustness of findings of government responses. Altmetric: 1706
Future Directions: From Observation to Translation
Personalized Glucose Trajectories (SSM-CGM) Isaac et al., arXiv, 2025 (NeurIPS Workshop) A “state-space” machine learning model that allows individuals to run “what-if” simulations on how their behavior affects blood sugar in real-time.
Plasma Proteomics & Lifestyle Exposome Isaac et al., medRxiv, 2025 Developed the Human Exposomic Architecture of the Proteome (HEAP) to show how lifestyle modifications target the same biological pathways as modern therapeutics.
Exposome vs. Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Prognosis Ellis et al., medRxiv, 2025 A head-to-head comparison proving that low-cost, scalable assessments of modifiable risk are as effective as invasive biomarkers for AD screening in asymptomatic populations.
Op-eds
Publication List
Check out Harvard Catalyst or Google Scholar for an updated list!